| Molecular phylogeny of the genus Echinopsis (Cactaceae) |
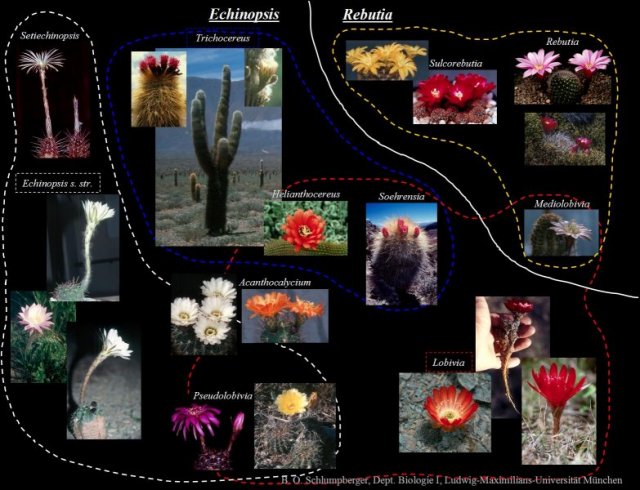
| The genus Echinopsis is one of the largest and morphologically most diverse cactus genera, including
formerly independent genera such as Helianthocereus, Lobivia, Pseudolobivia, Soehrensia and Trichocereus. Currently about 150
Echinopsis species are accepted, with about 500 synonymous names. Species of Echinopsis occur in Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay,
Argentina, Bolivia, Peru and Chile, and inhabit a wide range of habitats: from the lowlands of the Pampa and Chaco regions to
the Puna at ca. 4500 m, including all types of semi-arid to arid biotopes. The center of diversity for this genus is located in
the Andes from northern Argentina to southern Peru. Echinopsis comprises solitary or group-forming, tiny to barrel-like
globular cacti, as well as treelike columnar species. Molecular phylogenetic research is needed to clarify the delineation of
infrageneric groups down to the species level, the relation genera like Rebutia, and the position of the genus within the tribe
Trichocereeae. |
For enlargement (1565 x 1200 pixels = 305,072 bytes) click on the poster. |
|